In this tutorial we are using Helyx as a front end for OpenFoam to simulate the mixing of two gases. The complete workflow is displayed, from the STL modeling in Blender, Helyx to the postprocessing with Paraview is available at this page. The simulation start with all air within a cylinder . Then the air will be displaced by an inflow of Gas2, which also mixes with the air. The inflow comes through the inner pipe. The top lid of the cylinder is used as an outlet.
The result of the simulation is on YouTube . You can download the case and simulate the InterFoam[2].
By loading the video, you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
Learn more
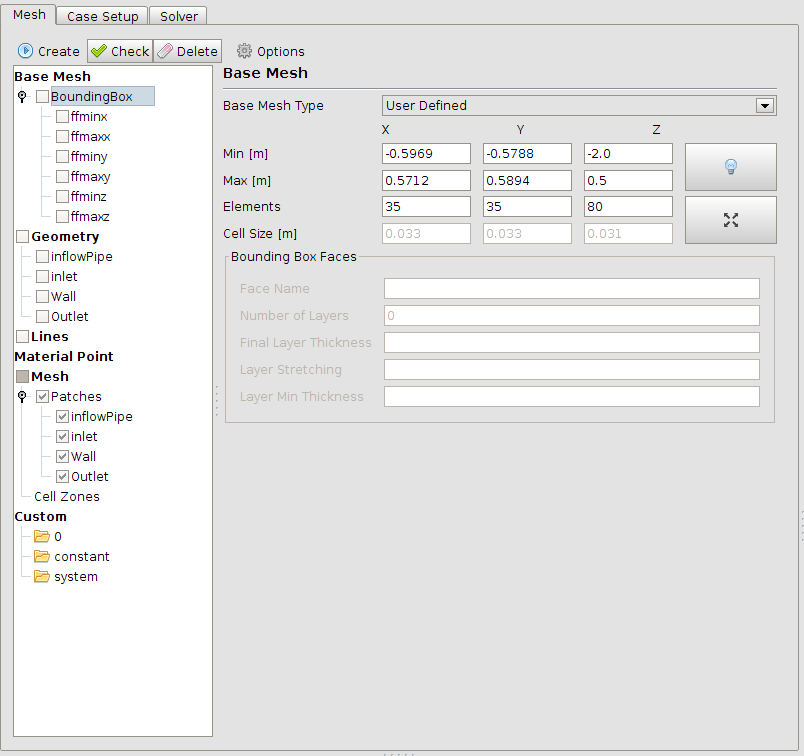
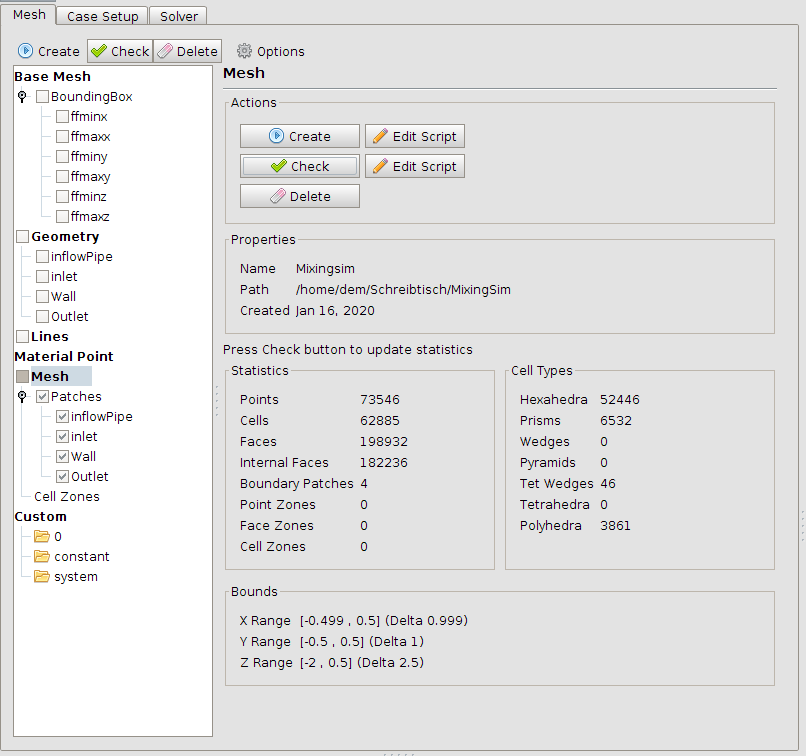
The first step is to load the geometry al STL files into snappyHexMesh. Then a base mesh is generated out of blockMesh. The parameters are shown in the images below. The meshing is done with a refinement at the walls of the inlet-pipe. checkMesh gives a quick overview if the mesh is alright.
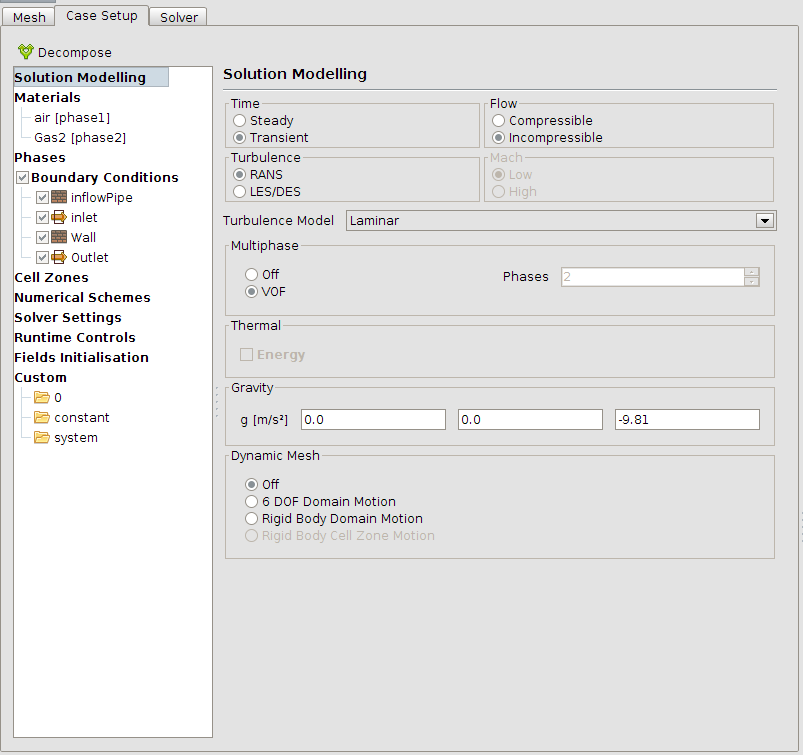
In the next step the type of simulation will be defined. In this case a multi-phase flow is used. The solver will be interFoam. The values which have to be set are shown in the image below.
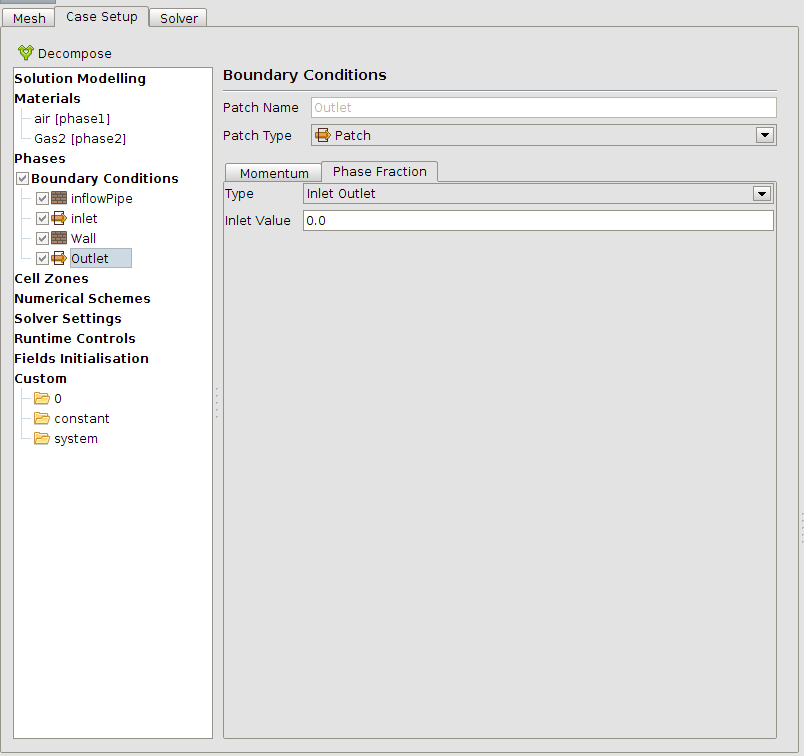
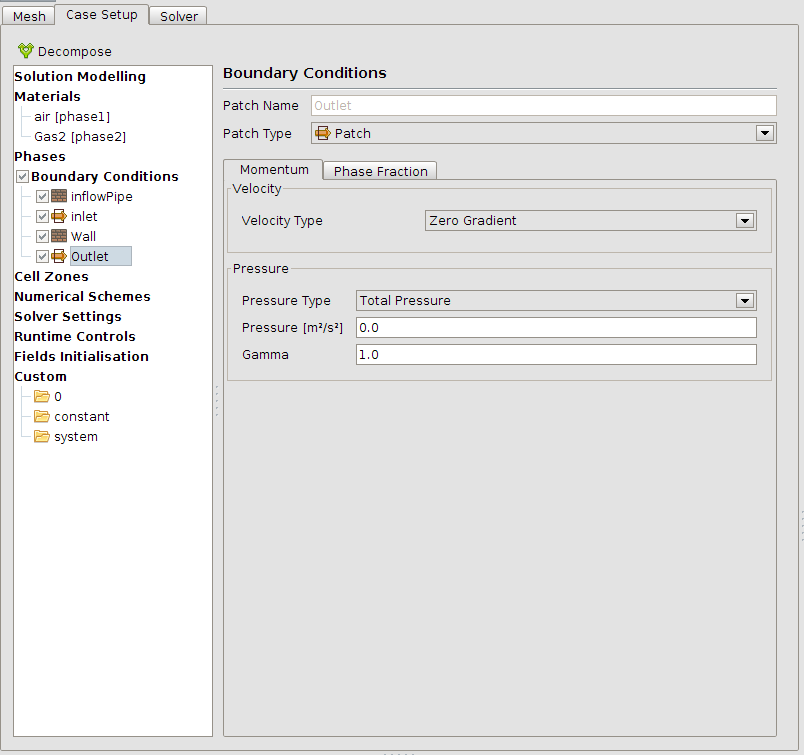
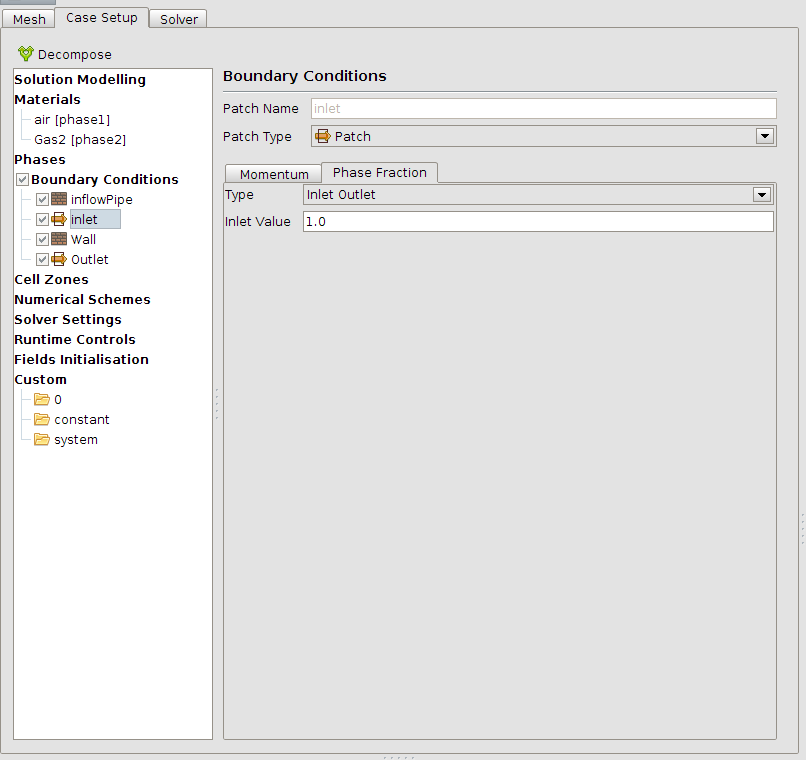
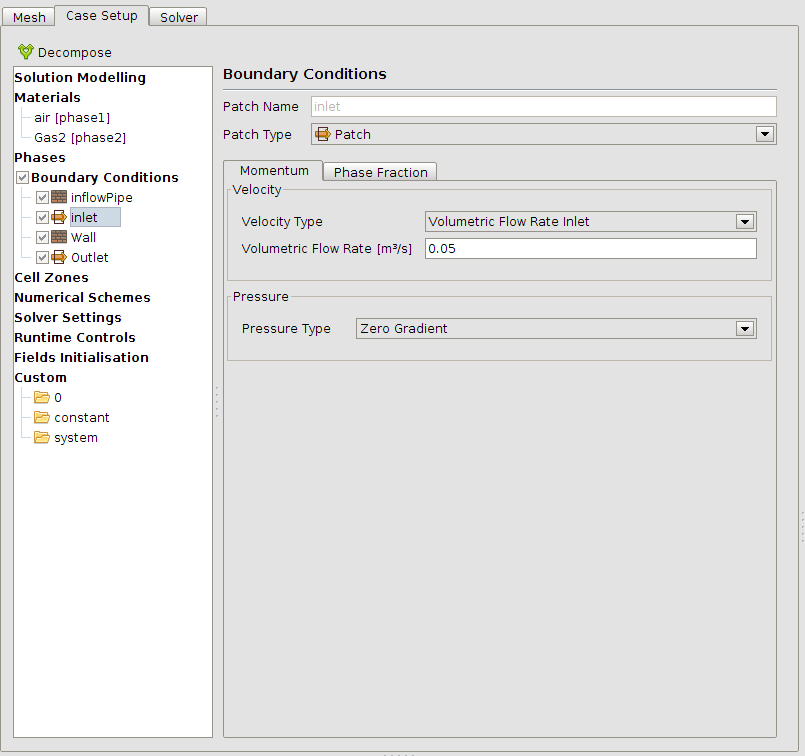
The boundary conditions must be set next. The outlet is set to Phase Fraction: “Inlet Outlet” = 0 which means that a potential back flow will be air. The inflow is from type Gas2 (this has the same properties in this simulation like air).
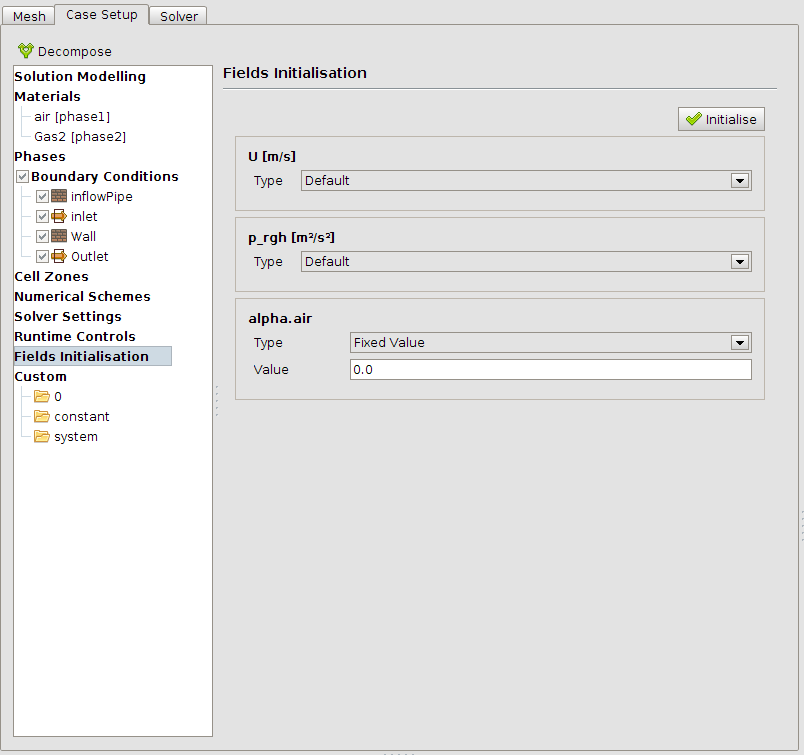
The field must be initilised with one gas. In this case this will be 0 which is air. With functions in openFoam the field initialisation can also be used to set only a part of the valome to a certain value. Here this coud be a partly filling of the cylinder with one or the other fluid. However, the cylinder is filld only with air in this simulation.
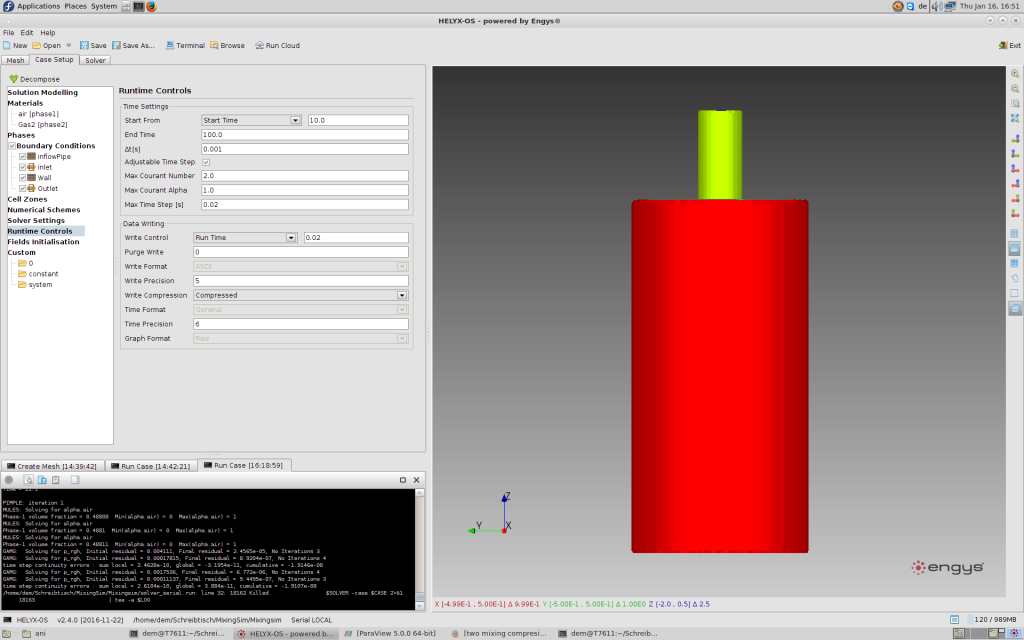
At last the solver settings must be set and the runtime controls have to be defined. A timestep of 0.001 s should be small enough here. It’s possible to use a Adjustable time step to get the simulation always calculating on the highest efficency. In theroy time step will be decreased if the convcergence is to low and it will be increased if the convergence is good enough. Here the time step will be choosen from the courant number which will saty the same. The Courant number is definet as how many cells the fuid can travel during one time step. For example if a cell has an edge length of 1 mm x 1 mm x 1 mm and the fluid ist travelling 10 mm / s at this cell that the Courant number will be 10. If the Max Courant Number is set to 2 the algorithm will divide the actual time step by 5 to match the max. Courant number.
 Privacy Preference
Privacy Preference
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.

Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Provider | Owner of this website |
| Purpose | Saves the visitors preferences selected in the Cookie Box of Borlabs Cookie. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Expiry | 1 Year |
Marketing cookies are used by third-party advertisers or publishers to display personalized ads. They do this by tracking visitors across websites.
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Google LLC |
| Purpose | Cookie by Google used for website analytics. Generates statistical data on how the visitor uses the website. |
| Privacy Policy | https://policies.google.com/privacy?hl=en |
| Host(s) | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Expiry | 2 Years |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | YouTube |
| Purpose | Used to unblock YouTube content. |
| Privacy Policy | https://policies.google.com/privacy?hl=en&gl=en |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Expiry | 6 Month |